08
2025
-
12
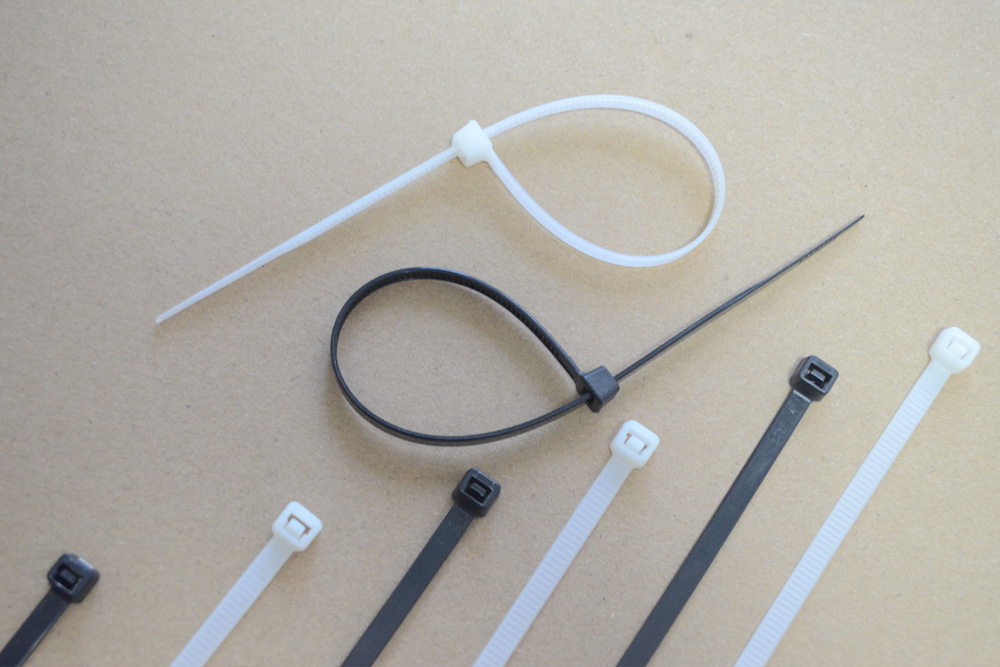
Selection of plastic cable ties for gardening
Author:
Selecting the Right Plastic Cable Ties for Gardening: A Size Guide
Understanding the Role of Dimensions in Plant Support
The effectiveness of plastic cable ties in gardening hinges on matching their dimensions to the specific needs of plants. Length determines how much space the tie can cover, while width influences its load-bearing capacity. For instance, securing thin tomato stems to stakes requires shorter ties (100–150mm), whereas bundling multiple grapevine branches demands longer options (300–400mm). Width selection follows a similar logic: narrow ties (2–4mm) work for lightweight foliage, while wider variants (6–8mm) resist pulling forces from heavy fruits or wind exposure.
A common mistake is overestimating tie strength. A 3mm-wide tie may seem sufficient for a young sapling, but as the plant grows, its weight and wind resistance increase. Upgrading to a 5mm-wide tie ensures long-term stability without frequent replacements. This principle applies to both indoor and outdoor settings—even potted plants benefit from properly sized ties when trained to climb trellises.
Matching Tie Length to Plant Growth Patterns
Plants exhibit diverse growth habits, from compact shrubs to sprawling vines. Short ties (100–200mm) excel in confined spaces, such as attaching herbs to small stakes or organizing seedling trays. Medium-length ties (250–350mm) strike a balance for mid-sized plants like roses or peppers, offering flexibility to adjust as stems elongate. For large-scale applications like securing fruit tree branches or creating bamboo fences, ties exceeding 400mm provide the necessary reach.
Consider the growth cycle when selecting lengths. Fast-growing plants like morning glories may require ties with 20–30% extra length to accommodate rapid stem extension. Conversely, slow-growing succulents need minimal adjustment, making shorter ties more economical. Always leave 10–15mm of slack after fastening to prevent constriction as plants swell with water or nutrients.
Evaluating Width for Structural Integrity
Width directly correlates with a tie’s tensile strength, which is critical for withstanding environmental stressors. Narrow ties (2–3mm) typically handle loads up to 10kg, suitable for lightweight tasks like bundling gardening tools or securing netting. Medium-width ties (4–5mm) increase capacity to 20–30kg, ideal for mid-weight applications such as training climbing beans or stabilizing small trees. Wide ties (6–8mm) offer 50kg+ resistance, making them indispensable for heavy-duty uses like anchoring trellises or supporting large fruit clusters.
Material composition amplifies width’s impact. Nylon ties, known for their elasticity, maintain strength even when bent at sharp angles, whereas rigid PVC ties may crack under similar stress. This durability difference explains why nylon ties of the same width often outperform PVC alternatives in load tests. For example, a 5mm nylon tie can secure a 25kg pumpkin vine, while a 5mm PVC tie might fail under the same weight.
Advanced Considerations for Specialized Gardening Needs
Certain gardening scenarios demand tailored approaches to tie selection. In hydroponic systems, where roots grow exposed, ultra-thin ties (1–2mm) minimize contact area to avoid damaging delicate root hairs. For arid climates, UV-resistant ties prevent degradation from prolonged sun exposure, extending their lifespan beyond standard models.
Eco-conscious gardeners may prioritize biodegradable ties made from plant-based polymers. These ties decompose within 1–2 years, reducing plastic waste in compost heaps. However, their lower tensile strength (typically 5–15kg) limits them to light-duty uses like securing seedling labels or organizing twine.
Finally, reusable ties with adjustable lengths—achieved through sliding buckles or multiple locking points—offer versatility for dynamic gardening projects. A single adjustable tie can replace several fixed-length options, simplifying inventory management while accommodating plants at various growth stages.
plastic cable ties
Hot News
2025-12-08
Selection of plastic cable ties for gardening
The effectiveness of plastic cable ties in gardening hinges on matching their dimensions to the specific needs of plants. Length determines how much space the tie can cover, while width influences its load-bearing capacity. For instance, securing thin tomato stems to stakes requires shorter ties (100–150mm), whereas bundling multiple grapevine branches demands longer options (300–400mm). Width selection follows a similar logic: narrow ties (2–4mm) work for lightweight foliage, while wider variants (6–8mm) resist pulling forces from heavy fruits or wind exposure.
2025-12-08
Recommended specifications of plastic cable ties for home storage
When selecting plastic cable ties for home organization, material composition directly impacts durability and functionality. Nylon-based cable ties, engineered from polyamide (PA6 or PA66), offer superior resistance to temperature fluctuations (-40°C to 85°C) and physical stress. These ties maintain flexibility even after repeated bending, making them ideal for outdoor applications like securing garden hoses or bundling patio furniture.
2025-12-05
The specifications of plastic cable ties for vibration scenarios are compatible
When securing components in environments with constant or intermittent vibration, choosing the correct plastic cable tie specifications is critical to ensuring long-term reliability and safety. Vibration can cause standard cable ties to loosen, fatigue, or break over time, leading to equipment damage or operational disruptions. This guide explores key factors to consider when selecting cable ties for vibration-heavy settings, covering material properties, mechanical design, and installation techniques.
2025-12-05
Material selection for plastic cable ties in chemical environments
When selecting plastic cable ties for chemical environments, the choice of material directly impacts performance, durability, and safety. Different chemical agents—such as acids, alkalis, solvents, and salts—pose unique challenges, requiring materials with tailored resistance properties. This guide explores three primary material options for chemical-resistant cable ties, analyzing their strengths, limitations, and ideal applications.